Basic grammar for revision
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Basic grammar for revision", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
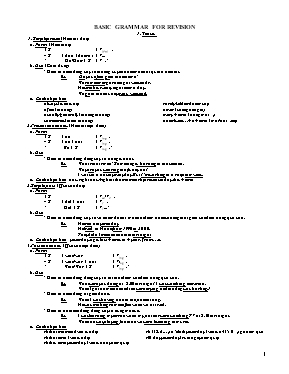
BASIC GRAMMAR FOR REVISION 1. Tense: 1. Simple present(Hiện tại đơn) a. Form: (Hình thức) + S + V(s/es) - S + don’t/ doesn’t + V... ? Do/Does + S + V? b. Use: (Cách dùng) * Diễn tả hành động xảy ra thường xuyên hoặc một thói quen ở hiện tại. Ex: Do you often go to the cinema? We sometimes go sailing at weekends. He smokes twenty cigarettes a day. We go to the country every weekend. c. Cách nhận biết: always (luôn luôn) rarely/seldom (hiếm khi) often (thường) never (không bao giờ) usually/generally (thường thường) every + time (hằng, mọi,) sometimes (thỉnh thoảng) once/twice+ a + time (một/hailần) 2. Present continous: (Hiện tại tiếp diễn) a. Form: + S + be + Ving - S + be + not + Ving ? Be + S + Ving? b. Use: * Diễn tả hành động đang xảy ra trong lúc nói. Ex: What’s that smell? Something is burning in the kitchen. Why are you wearing that funny hat? I work in a bakery everyday. But I’m working in a shop this week. c. Cách nhận biết: now, right now/right at the moment/at present, today, this + time 3. Simple past: (Quá khứ đơn) a. Form: + S + Ved/V2 - S + did + not + V1 ? Did + S + V1...? b. Use: * Diễn tả hành động xảy ra và chấm dứt tại một thời điểm hoặc khoảng thời gian xác định trong quá khứ. Ex: He met her yesterday. He lived in Hanoi from 1990 to 2000. They didn’t meet each other last night. c. Cách nhận biết: yesterday, ago, last + time, in + year, fromto. 4. Past continuos: (Quá khứ tiếp diễn) a. Form: + S + were/was + Ving - S + were/was + not + Ving ? Were/Was + S + Ving? b. Use: * Diễn tả hành động đang xảy ra tại thời điểm xác định trong quá khứ. Ex: What were you doing at 8.00 last night? I was watching television. When I got home, the children were crying and the dog was barking.1 * Diễn tả hành động bị gián đoạn. Ex: While I was having a bath, the phone rang. He was making some coffee when we arrived. * Diễn tả hai hành động đang xảy ra cùng một lúc. Ex: I was learning my lesson while my parents were watching TV at 8.30 last night. While he was playing football, we were listening to music. c. Cách nhận biết: At that moment (vào lúc đó) At 4(5, 6,) o’clock yesterday (vào lúc 4(5, 6)giờ hôm qua At that time (vào lúc đó) All day yesterday (suốt ngày hôm qua) At this time yesterday (vào lúc này hôm qua) At this last night (vào lúc này tối qua) 5. Present perfect: (Hiện tại hoàn thành) a. Form: + S + have/has + Ved /V3 - S + have/has + not + Ved /V3 ? Have/Has + S + Ved /V3? b. Use: * Dùng để chỉ hành động xảy ra trong quá khứ và kéo dài đến hiện tại. Ex: I have learnt English for 5 years. My mother has decorated the house since yesterday. He has seen that actor many times. c. Cách nhận biết: for (suốt) recently/lately (gần đây) since (kể từ) never up to now/so far/until now/up to present (cho tới nay) still (vẫn) for ages (đã lâu) notyet (chưa) already (rồi) several times = many times (nhiều lần) NOTES: * FOR + khoảng thời gian Ex: for 3 hours, for a long time * SINCE + mốc thời gian Ex: since 1968, since last Chrismas 6. Present perfect continuos: (Hiện tại hoàn thành tiếp diễn) a. Form: + S + have/has + been + Ving - S + have/has + not + been + Ving ? Have/Has + S + been + Ving? b. Use: * Nhấn mạnh sự liên tục của hành động kéo dài từ trong quá khứ và vẫn còn đang tiếp diễn. Ex: I’ve been working for the same company for twelve years. How long have you been playing football? 7. Past perfect: (Quá khứ hoàn thành) a. Form: + S + had + Ved/V3 - S + had + not + Ved/V3 ? Had + S + Ved/V3? b. Use: * Diễn tả hành động xảy ra trước một hành động khác hoặc thời điểm khác trong quá khứ. c. Cách nhận biết: before, after, by the time, when, as soon as. Ex: My parents had already eaten by the time I got home. Until yesterday, I had never heard about it. 8. Past perfect continuos: (Quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn) a. Form: + S + had + been + Ving... - S + had + not + been + Ving... ? Had + S + been + Ving? b. Use: * Dùng để nhấn mạnh tính liên tục của một hành động xảy ra trước một hành động khác hay một thời điểm khác cũng trong quá khứ. Ex: She had been studying English before she came here for classes. The police had been looking for the criminal for two years before they caught him. 9. Simple future:(Tương lai đơn) a. Form: + S + will/shall + V(bare inf) - S + will/shall + not + V(bare inf) ? Will/Shall + S + V(bare inf)? b. Use: * Diễn tả hành động sẽ xảy ra tại một thời điểm nào đó trong tương lai: tomorrow, next + time Ex: He will finish his work tomorrow. We shall have our examination next month. * Diễn đạt một đề nghị, một yêu cầu, hay sự mời mọc (thường ở dạng câu hỏi). Ex: Will you go shopping with me now? 10. Future continnuos: (Tương lai tiếp diễn) a. Form: + S + will/shall + be + Ving - S + will/shall + be + not + Ving ? Will/Shall + S + be + Ving? b. Use: * Diễn tả hành động sẽ đang diễn ra tại một thời điểm xác định trong tương lai. Ex: Don’t phone at 8.00. I’ll be having supper. This time tomorrow I’ll be flying to New York. * Dùng để hỏi về những kế hoạch hay dự tính của người khác, nhất là khi chúng ta muốn cái gì đó hay muốn người nào làm điều gì đó. Ex: “Will you be using your bicycle this evening?” “No, you can take it” “Will you be passing the post office when you go out?” “Yes, why?” 11. Future perfect:(Tương lai hoàn thành) a. Form: + S + will/shall + have + Ved/V3 - S + will/shall + not + have + Ved/V3 ? Will/Shall + S + have + Ved/V3? b. Use: * Diễn tả hành động sẽ hoàn thành trước một hành động khác hoặc thời điểm khác trong tương lai. Ex: The taxi will have arrived by the time you finish dressing. By next Christmas, he will have lived in Dalat for 5 years 2. Verb forms: 1. List of verbs followed by Ving admit thừa nhận discuss thảo luận permit cho phép advise khuyên bảo dislike không thích postpone trì hoãn allow cho phép enjoy thích thú practise luyện tập, thực hành avoid tránh né, tránh xa encourage khuyễn khích quit bỏ, từ bỏ, ngừng nghỉ complete hoàn thành finish hoàn thành, kết thúc recommend đề nghị consider cân nhắc, xem xét forbid cấm đoán resent giận, oán giận continue tiếp tục give up từ bỏ resist cưỡng lại, chống lại can’t help không thể không keep on cứ, cứ tiếp tục suggest đề nghị can’t stand không thể chịu được mention đề cập đến, nói về tolerate khoan dung, tha thứ delay hoãn lại mind chú ý, quan tâm understand hiểu deny phủ nhận miss bỏ lỡ worthless vô giá trị, vô dụng no use no point 2. List of verbs followed by to – infinitive: afford có đủ tiền fail quên, thất bại refuse từ chối agree đồng ý hesitate do dự seem trông có vẻ appear dường như hope hy vọng struggle đấu tranh, gắng sức arrange sắp đặt, thu xếp learn học swear thề ask yêu cầu manage xoay sở threaten đe doạ beg năn nỉ, cầu xin mean có ý, muốn nói volunteer tình nguyện consent ưng thuận offer đề nghị wait chờ đợi decide quyết định plan lập kế hoạch want muốn demand đòi hỏi prepare chuẩn bị wish ước muốn deserve đáng, xứng đáng pretend làm ra vẻ, giả vờ expect mong đợi promise hứa 3. List of verbs followed by an object + to – infinitive: advise khuyên bảo expect mong, đợi remind nhắc nhở allow cho phép forbid cấm, ngăn cấm require yêu cầu, đòi hỏi ask yêu cầu force bắt buộc, ép buộc teach dạy beg năn nỉ instruct chỉ dẫn, hướng dẫn tell bảo cause khiến cho, gây ra invite mời urge thúc, thúc giục challenge thách thức need cần want muốn convince thuyết phục order ra lệnh warn cảnh báo dare thách thức permit cho phép recommend đề nghị encourage khuyến khích persuade thuyết phục 4. List of verbs followed by either a Ving or a to – infinitive:(with a difference in meaning) stop: - stop + Ving: ngừng làm công việc đang làm. Ex: He was writing and when I came in, he stopped writing and looked at me. - stop + to inf: ngừng lại để làm một việc khác. Ex: He was speaking on the phone when the door bell rang. He stopped to answer the door. forget/remember: - forget/remember + Ving: quên hoặc nhớ điều gì đã xảy ra trong quá khứ. Ex: I remember playing with dolls when I was a child. I never forget winning the scholarship last year. - forget/remember + to inf: quên hoặc nhớ thực hiện trách nhiệm, bổn phận hay công việc nào đó trong hiện tại hoặc tương lai. Ex: I always remember to lock the front door before going to school. Don’t forget to phone me when you return home tomorrow. regret: - regret + Ving: tiếc điều gì đã xảy ra trong quá khứ. Ex: I regret lending him money. He never paid it back to me. - regret + to inf: tiếc là phải nói hoặc thông báo cho ai về điều gì không hay. Ex: I regret to tell you that you failed the college entrance examination. need: - need + Ving: (passive meaning) cần phải được. Ex: My house is rather old. It needs repainting. - need + to inf: cần phải làm điều gì (mà chưa làm được). Ex: She needs to study harder so that she can pass the final test. try: - try + Ving: thử làm điều gì để xem có được hay không. - try + to inf: cố gắng. 5. Special expressions followed by the ing – form have fun / have a good time: thích thú, vui vẻ. have trouble / have difficulty / have a hard time / have a difficult time: gặp khó khăn trong việc gì. spend / waste + (time) + Ving. sit / stand / lie + (place) + Ving. find / catch + object + Ving: thấy hay bắt gặp ai đang làm gì. to be no good / no use + Ving: vô ích. to be worth / worthwhile + Ving: đáng, xứng đáng. to be busy + Ving: bận làm gì. There is no point in + Ving can’t stand = can’t help: không thể không. 6. Go Ving: go birdwatching : đi xem triển lãm chim go camping : đi cắm trại. go dancing : đi khiêu vũ. go fishing : đi câu cá. go hiking : đi bộ. go hunting : đi săn. go jogging : đi chạy bộ. go mountain climbing : đi leo núi. go sailing :đi chèo thuyền. go shopping : đi mua sắm. go window shopping : đi dạo. go swimming : đi bơi. 7. S + V + O + bare infinitive/Ving: feel : cảm thấy. hear : nghe. listen toa : lắng nghe. notice : chú ý. observe : quan sát. perceive : cảm nhận see : thấy. watch : xem. hark at : nghe kìa. smell : ngửi. look at : nhìn. 8. V + O + bare infinitive: have: nhờ make: bắt let: để, cho phép help: giúp đỡ Những trường hợp đặc biệt: It is time + S + Ved/II (quá khứ): Đến giờ để chúng ta làm gì. Ex: It’s time we went. S + would rather + S + Ved/II (quá khứ): Ai muốn / thích ai làm gì hơn. Ex: I would rather you did the test well. S + suggest + Ving: Ai đề nghị nên làm chuyện gì. Ex: I suggest fixing the faucet. S + suggest + (that) + S + should + V: Ai đề nghị ai nên làm chuyện gì. Ex: I suggest that we should turn off the faucet. 3. Tag questions: Affirmative statement, negative tag? Negative statement, affirmative tag? Ex: Hoa makes the questions, doesn’t she? They won’t answer the questions, will they? Helen can speak English very well, can’t she? Nam didn’t agree with you, did he? My mother is very beautiful, isn’t she? My father didn’t go to the cinema, did he? Những trường hợp đặc biệt: * Phần đuôi của “I am” là “Aren’t I”. Eg: I’m going to do it again, aren’t I? * Imperatives and Requests (Câu mệnh lệnh và câu yêu cầu) - Imperatives: + Có phần đuôi là “won’t you” và diễn tả lời mời: Eg: Take you seat, won’t you? (Mời ông ngồi) + Có phần đuôi là “”will you” và diễn tả yêu cầu: Eg: Open the door, will you? (Xin vui lòng mở cửa) - Requests: Eg: Please keep silent, will you? (Vui lòng giữ im lặng) Please don’t make noise, will you? (Xin vui lòng đừng làm ồn) + Phần đuôi của câu với “Let’s + V”: là “shall we”: Eg: Let’s go swimming, shall we? (Chúng ta đi bơi nhé) + “Nothing” được thay thế bằng “It” ở câu hỏi đuôi: Eg: Nothing gives you more pleasure than listening to music, does it? + No one, Nobody, anyone, anybody, someone, somebody, everybody, everyone được thay thế bằng “They”: Eg: Someone remembered to leave the messages, didn’t they? Chú ý: + Nothing, Nobody được dùng trong mệnh đề chính, động từ ở câu hỏi đuôi sẽ phải ở dạng thức xác định. Eg: Nobody phoned while I was out, did they? + This / That được thay thế bằng “It”. Eg: This won’t take long, will it? + These / Those được thay thế là “They”. Eg: Those are nice, aren’t they? 4. Comparision of adjectives and adverbs 1. So sánh bằng: + Khẳng định: AS + Adj/Adv + AS : bằng, như Ex: My sister is as tall as me. + Phủ định: NOT SO/AS + Adj/Adv + AS : khôngbằng Ex: She doesn’t work so/as hard as her friends (do). 2. So sánh hơn: + Tính từ và trạng từ ngắn: Adj / Adv + -ER + THAN : hơn Ex: Ann is taller than me. + Tính từ và trạng từ dài: MORE + Adj/Adv + THAN Ex: This exercise is more difficult than that one. * (Trạng từ) ngắn gồm các tính từ có một âm tiết và các tính từ có hai âm tiết mà tận cùng là: -y, -ow, -er, -le, -et happy – happier narrow – narrower quiet – quieter clever – cleverer simple – simpler * (Trạng từ) ngắn tận cùng là một phụ âm, trước nó là một nguyên âm thì gấp đôi phụ âm cuối trước khi thêm ER hot – hotter big = bigger 3. Superlative (So sánh nhất): + Tính từ và trạng từ ngắn: THE + Adj/Adv + -EST : nhất Ex: Nile is the longest river in the world. + Tính từ và trạng từ dài: THE MOST + Adj/Adv Ex: That was the most interesting story I’ve ever read. 4. Những trường hợp bất quy tắc: Adj/Adv Comparative Superlative good/well better the best bad/badly worse the worst many/much more the most little less the least far farther/further the farthest/the furthest Ex: They all behaved badly, but Peter behaved the worst. Annie feels much better today. 5. Double Comparison (So sánh kép): * So sánh kép để miêu tả sự việc ngày càng phát triển: Short Adj: Adj + -ER and Adj + -ER. Long Adj: More and more + Adj. Ex: The standard of living is getting better and better The tests are more and more difficult * So sánh kép để miêu tả hai sự kiện cùng phát triển song song nhau, thay đổi ở sự kiện này sẽ kèm theo thay đổi ở sự kiện kia: The + adj/adv + er, the + adj/adv + er The more + adj/adv, the more +adj/adv Ex: The more you learn, the better you know about the world. 5. Relative clauses Chức năng Mệnh đề quan hệ giới hạn Mệnh đề quan hệ không giới hạn Chủ ngữ Người WHO/THAT WHO Vật WHICH/THAT WHICH Tân ngữ Người WHOM/THAT WHOM Vật WHICH/THAT WHICH Sở hữu Người WHOSE WHOSE Vật WHOSE/OF WHICH WHOSE/OF WHICH 1. Mệnh đề quan hệ giới hạn: a) Relative pronouns: WHO – WHOM – WHICH – WHOSE – THAT 1. The woman is my mother. She wears a hat. The woman who/that wears a hat is my mother. 2. My mother is the person. I always think of her. My mother is the person whom/that I always think of. 3. The bicycle is beautiful. You are looking at it. The bicycle which/that you are looking at is beautiful. 4. The book is my teacher’s. It is on the table. The book whose/that on the table is my teacher’s. 5. He is the boy. His father is the director of this company. He is the boy whose father is the director of this company. b) Relative adverbs: WHERE – WHEN – WHY 1. WHERE: được dùng để thay thế “giới từ + which”: “in which, at which, on which,” khi nói về nơi chốn. Ex: I went to the office. My father works in the office. I went to the office in which my father works. I went to the office where my father works. 2. WHEN: được dùng để thay thế “giới từ + which”: “in which, at which, on which,” khi nói về thời gian. Ex: You can visit me on Sundays. I am usually free on Sundays. You can visit me on Sundays on which I am usually free. You can visit me on Sundays when I am usually free. 3. WHY: được dùng để thay thế “for + which” khi nói về lý do. Ex: He refused my invitation. The reason is unknown. The reason why he refused my invitation is unknown. NOTE: “where, when, why” không bao giờ đi sau giới từ. 2. Mệnh đề quan hệ không giới hạn: là mệnh đề bổ sung, đặt sau danh từ đã được xác định và được ngăn cách với mệnh đề chính bởi một hoặc hai dấu phẩy. Ex: Michael Jackson is an American singer. I saw him on TV yesterday. Michael Jackson, whom I saw on TV yesterday, is an American singer. NOTES: “That” thường được dùng trong các trường hợp sau: - Khi danh từ đi trước chỉ người và vật. Ex: The girls and flowers that he painted were vivid - Sau so sánh nhất, khi danh từ đi trước làm tân ngữ và sau những từ như: the first, the last, the only, the very, any, all, nothing, anything, everything, few, nobody, Ex: You are the person that I have been looking for. She is the ugliest girl that I’ve ever seen. I have never seen anvone that is as lovely as she. “That” không bao giờ được dùng trong các trường hợp sau: - Đại từ quan hệ có giới từ đứng trước. Ex: The house in which. I live is my father’s. That is the man from whom I borrowed the car. - Mệnh đề quan hệ không giới hạn Ex: Viet Nam, which is in the south – east Asia, exports rice. Trong mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định (không giới hạn), danh từ xác định thường là: - Danh từ riêng: Hong, Nam, Mr. Spears, Mrs. Smith, - Đại từ chỉ định: this, that, these, those - Tính từ sở hữu: my, your, his, her, our, their Ex: Mr. Pike is very nice. He is my neighbor. Mr. Pike, who is my neighbor, is very nice. This matter is of great importance. You should pay attention to it. This matter, to which you should pay attention, is of great importance. Do you see my pen? I’ve just written the lesson with it. Do you see my pen, with which I’ve just written the lesson. 6. Structures of “use” Be/Get used to + Ving/Noun/Noun phrases = be accustomed to Ving = get used to Ving: quen với, thích nghi với. Ex: Women are used to being Independent. I am used to hot weather. Used to + bare infinitive: đã từng, thường (thói quen trong quá khứ) (S didn’t use to + V1 / Did + S + use to + V1?) Ex: He used to smoke a lot of cigarette. Use + Noun: dùng Ex: I have used this book for many years. Be used for + Ving / Be used to + V1: được dùng để (công dụng của một vật) Ex: Money is used for buying and selling goods = Money is used to buy and sell goods. 7. Wish clauses: 1. Mong ước không thể xảy ra ở tương lai would + V 2. Mong ước trái sự thật ở hiện tại Quá khứ đơn (Be were) 3. Mong ước trái sự thật ở quá khứ Quá khứ hoàn thành Ex: I wish I would fly to Hanoi tomorrow. She wish she had enough time to study now. They wish thay had come to the party last night. 8. Conditional sentences Loại If clauses Main clauses 1. Điều kiện có thể xảy ra ở tương lai Simple present will/shall+ V1 2. Điều kiện không thể xảy ra ở hiện tại Simple past (be were) would/should+V1 3. Điều kiện không thể xảy ra ở quá khứ Past perfect would/should+have + V3/Ved NOTES: 1. Unless + Ifnot (nếu không, trừ phi) Ex: Unless it rains, we will go to the movies + If it doesn’t rain, we will go to the movies. Unless they attended class regularly, they couldn’t understand the lesson. 2. As long as / provided / providing (that): với điều kiện là Ex: You can borrow my book as long as you use it carefully. You can play providing (that) you don’t make so much noise. 3. Suppose, supposing: giả sử Ex: Supposing you won a lot of money, what would you do? 4. In case: phòng khi, trong trường hợp Ex: Take an umbrella wish you in case it rains. 9. Passive voice Active: Mr. Smith taught English Passive: English was taught by Mr. Smith BẢNG TÓM TẮT CÁC THÌ Ở THỂ BỊ ĐỘNG Tense Active Passive 1. Simple present S + V(s/es) S + am/is/are + V3/Ved 2. Present continous S +am/is/are + Ving S + am/is/are + being + V3/Ved 3. Simple past S + V2/Ved S + was/were + V3/Ved 4. Past continous
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 basic_grammar_for_revision.doc
basic_grammar_for_revision.doc