Ngữ pháp và bài tập Unit 8 môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 (Thí điểm)
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Ngữ pháp và bài tập Unit 8 môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 (Thí điểm)", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
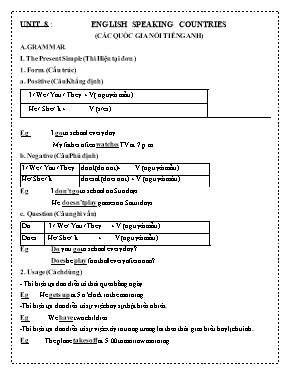
UNIT 8 : ENGLISH SPEAKING COUNTRIES (CÁC QUỐC GIA NÓI TIẾNG ANH) A.GRAMMAR. I. The Present Simple (Thì Hiện tại đơn ) 1. Form. (Cấu trúc) a. Positive (Câu Khẳng định) I / We / You / They + V( nguyên mẫu) He / She / It + V (s/es) Eg I go to school every day. My father often watches TV at 7 p.m b. Negative (Câu Phủ định) I / We / You / They don't (do not)+ V (nguyên mẫu) He/ She / It doesn't (does not) + V (nguyên mẫu) Eg I don’t go to school on Sundays. He doesn’t play games on Saturdays. c. Question (Câu nghi vấn) Do I / We / You / They + V (nguyên mẫu) Does He/ She / It + V (nguyên mẫu) Eg Do you go to school every day ? Does he play football every afternoon? 2. Usage (Cách dùng) - Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả thói quen hằng ngày. Eg He gets up at 5 o’clock in the morning. -Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả sự việc hay sự thật hiển nhiên. Eg We have two children. -Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả sự việc xảy ra trong tương lai theo thời gian biểu hay lịch trình. Eg The plane takes off at 5.00 tomorrow morning. + Các trạng từ đi kèm với thì hiện tại đơn Every day / week / month..(Hằng ngày / tuần / tháng...) Always : luôn luôn Usually : thường xuyên Often : thường Sometimes : thỉnh thoảng Seldom : hiếm khi Never : không bao giờ NOTE (CHÚ Ý) Những động từ tận cùng là : o, s , ch , sh, x, z , ta thêm es Eg go -> goes watch -> watches wash -> washes fix -> fixes - Những động từ tận cùng là y mà đằng trước là nguyên âm ( u, e ,o , a, i) ta để nguyên y rồi thêm s Eg play -> plays say -> says Những động từ tận cùng là y mà đằng trước là phụ âm ta đổi y thành i rồi thêm es Eg study -> studies fly -> flies II. The Present Continuous (Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn) 1. Form (Cấu trúc) a. Câu khẳng định I + am + V-ing He / She / It + is + V-ing We / You / They + are + V-ing Eg I am learning English at the moment. He is playing football now. We are listening to music at this time. b. Câu phủ định I + am + not + V-ing He / She / It + is + not + V-ing We / You / They + are + not + V-ing Eg I am not learning English at the moment. He is not playing football now. c. Câu nghi vấn. Am + I + V-ing Is + He / She / It + V-ing Are + You / We / They + V-ing Eg Are you learning English at the moment? Is He playing football now ? 2. Usage. (Cách dùng) -Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn dùng để diễn tả một hành động đang xảy ra tại thời điểm nói trong hiện tại. Eg She is talking to her teacher about that plan. - Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn đề cập đến những thói quen xấu gây khó chịu cho người khác, thường đi cùng trạng từ “ always “ hoặc “constantly”. Eg He is always leaving his dirty socks on the floor. - Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn dùng để diễn tả những tình huống đang thay đổi. Eg Her son is getting better. -Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn diễn tả một kế hoạch chắc chắn sẽ xảy ra trong tương lai (thường đi cùng với trạng từ chỉ thời gian trong tương lai). Eg. I am studying English next summer. Các trạng từ đi kèm với thì hiện tại tiếp diễn. Now : bây giờ At the moment : ngay bây giờ At this time : vào lúc này Today : hôm nay Be quiet : Hãy yên lặng Listen : Nghe này III. The Present Perfect (Hiện tại hoàn thành) 1. Form (Cấu trúc) a. Câu khẳng định I /You/ We/ They + have + Ved / Vpp He / She / It + has + Ved /Vpp Eg I have lived in Thanh Hoa city since 1987 He has bought a new car for 2 weeks. b. Câu phủ định I /You/ We/ They + have + not + Ved / Vpp He / She / It + has + not + Ved /Vpp Eg I haven’t lived in Thanh Hoa city since 1987 He hasn’t bought a new car for 2 weeks. c. Câu nghi vấn Have + I /You/ We/ They + Ved / Vpp Has + He / She / It + Ved /Vpp Eg Have you been to England ? Has Ba gone to Sam Son beach? 2. Usage (Cách dùng). - Thì hiện tại hoàn thành diễn tả sự việc xảy ra trong quá khứ và kéo dài đến hiện tại. Eg I have learnt English for 15 years. She has lived here since 2016 - Thì hiện tại hoàn thành diễn tả sự việc vừa mới xảy ra nhưng không đề cập đến thời gian ,thường dùng với các từ như “ just, already hay yet. Eg She has just come. They haven’t arrived yet. -Thì hiện tại hoàn thành dùng để nói về các sự việc vừa mới xảy ra và hậu quả của nó vẫn còn ảnh hưởng đến hiện tại. Eg He has just washed his car, so it looks very clean now. -Thì hiện tại hoàn thành khi nói về trải nghiệm hay kinh nghiệm , thường đi kèm với ever/ never. Eg Have you ever been to London ? I have never seen that movie before. Những trạng từ chỉ thời gian đi kèm với thì hiện tại hoàn thành: Ever : bao giờ Never : không bao giờ So far : cho đến bây giờ / nay Serveral times : vài lần rồi Just : vừa mới’ Already : rồi Yet : chưa IV. The present simple for future.( Thì hiện tại đơn mang ý nghĩa tương lai) 1. Form. (Cấu trúc) a. Positive (Câu Khẳng định) I / We / You / They + V( nguyên mẫu) He / She / It + V (s/es) Eg I go to school every day. My father often watches TV at 7 p.m b. Negative (Câu Phủ định) I / We / You / They don't (do not)+ V (nguyên mẫu) He/ She / It doesn't (does not) + V (nguyên mẫu) Eg I don’t go to school on Sundays. He doesn’t play games on Saturdays. c. Question (Câu nghi vấn) Do I / We / You / They + V (nguyên mẫu) Does He/ She / It + V (nguyên mẫu) Eg Do you go to school every day ? Does he play football every afternoon? 2. Usage (Cách dùng) - Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả thói quen hằng ngày. Eg He gets up at 5 o’clock in the morning. -Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả sự việc hay sự thật hiển nhiên. Eg We have two children. Ngoài cách dùng ở trên , thì hiện tại đơn còn mang ý nghĩa tương lai khi nói về thời gian biểu, chương trình , lịch trình , và trong các trạng từ chỉ thời gian cụ thể.. Eg The plane takes off at 5.00 tomorrow morning. B.EXERCISES. A.LISTENING Listen to the conversation between Nick and Phong .Decide the statements are true or false? 1. Nick is at national summer camp. F 2. Your English has improved a lot. T 3. He has made many friends from English T speaking countries. 4. He can't practise English with native speakers. F 5. He comes back home on July 15th. T B.USE OF LANGUAGE. I. Find the word which has different sound in the part underlined. 1. A. wanted B. washed C. needed D. decided 2. A. ago B. boring C. explore D. story 3. A. come B. sot C. open D. cold 4. A. mention B. question C. action D. education 5. A. who B. when C. where D. what II. Find the word which has different stress pattern from the others. 1. A. coffee B. rupee C. trainee D. agree 2. A. symbolise B. Taiwanese C. guarantee D. kangaroo 3. A. Maltese B. festival C. degree D. unique 4.A. government B. celebrate C. nominee D. popular 5.A. Canadian B. introduce C. Guyanese D. absentee III. Find one word that does not belong to each group. 1. A. Chinese B.computerese C. Japanese D. Portuguese 2. A. international B. local C. national D. natural 3. A. Awesome B. Great C. Fantastic D. Sure 4.A. scenery B. landscape C. culture D. view 5.A. desert B. haunted castle C. loch D. puzzling world IV. Complete the sentences with words/ phrases from the V. Supply the correct tense of the words given in each blanket. Four countries ______________ (visit) by John so far. London ______________ (have) a population of eight million people. The Statue of Liberty in New York is a monument which ______________ (symbolize) freedom. Vietnam’s Independence Day ________________ (celebrate) on September 09th. We ______________ (visit) Sydney Opera House for several times. Some activities ______________ (prepare) to celebrate the lunar new year now. VI. Choose the correct answer A, B, or C to complete each of the sentences. 1.Alaska is perhaps the most state in the USA. It has over three million lakes. A. puzzling B. festive C. amazing 2.The old tradition of first- footing is still practiced today in .. A. Scottish B. Scots C. Scotland 3.In Canada, the serving of coffee at the end of an evening is a signal that it is time for .. A. visitors B. tourists C holiday makers 4.The Maori in New Zealand greet each other by .. their noses. A. punching B. touching C. blowing 5. Australia is composed of seven .. A. nations B. countries C. states 6.There is a red maple leaf on the of Canada. A. flag B. banner C. money VII. Read the passage and answer these questions below: England is not a large country. No town in England is very far from the sea, and many English families spend their summer holidays at the seaside. There are no high mountains in England, no very long rivers and very large forests. There are many towns in England. No town is very far from another. The English countryside between the towns is like a carpets of many colors. In Spring and summer, the fields, meadows and forests are light green or dark green, and the gardens are green , red, blue, yellow and white with flowers. Questions 1.Is England a large country? .................................................................................................................................................. 2. Where do many English families spend their summer holidays? .................................................................................................................................................. 3. Are there many towns in England? .................................................................................................................................................. 4. What is the English countryside like? .................................................................................................................................................. VI. Read the passage and do the tasks that follow Alaska is perhaps the most amazing state in the USA. It has coastlines facing both the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. This state has an incredible three million lakes. That’s four lakes per person living there. Many cities in Alaska cannot be reached by road, sea, or river. The only way to get in and out is by air, on foot, or by dogsled. That’s why Alaska has the busiest sea airport in the world, Lake Hood Seaplane Base. Nearly two hundred floatplanes take off and land on the water of this airport every day. It is a really fun scene to watch. Alaska is called the land of Midnight Sun because in summer, the sun does not set for nearly three months. But in winter the sun stays almost unseen. All Alaskans take special pride in their beautiful and unique state. 1. Alaska ___________. A. is another name for the USA B. is an island in the Pacific Ocean C. has coastlines facing both the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean 2. Which statement below is NOT CORRECT? A. In Alaska, the number of lakes is bigger than that of people. B. There is one lake for each person living there. C. Alaska has an incredibly high number of lakes. 3.Which method below can always be used to reach a place in Alaska? A. by air B. by road C. by river 4. In Alaska we can always see the sun ___________. A. in winter B. in summer C. every month of the year VIII. Rewrite the sentences below without changing their original meaning. Radioactive pollution is very dangerous. It can cause abnormal growth. [since] Leaves are damaged. The tree cannot get enough food energy to stay healthy. [because] I don’t have much money now, but I want to buy a house in PhuCuong. If Light pollution happens. There is a change in animals’ living patterns. If Acid rain is dangerous. Trees’ leaves are damaged. [because of] The Walt Disney Studios, the famous movie company, has produced hundreds of cartoons for children. Hundreds of cartoons for children
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 ngu_phap_va_bai_tap_unit_8_mon_tieng_anh_lop_8_thi_diem.docx
ngu_phap_va_bai_tap_unit_8_mon_tieng_anh_lop_8_thi_diem.docx