Lý thuyết Câu trực tiếp & Câu gián tiếp
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Lý thuyết Câu trực tiếp & Câu gián tiếp", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
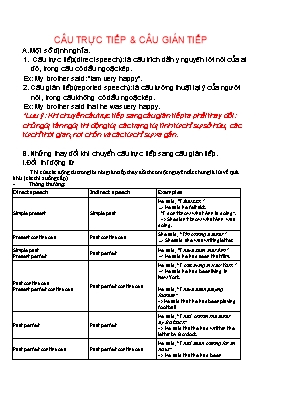
CÂU TRỰC TIẾP & CÂU GIÁN TIẾP Một số định nghĩa. Câu trực tiếp(direct speech): là câu trích dẫn y nguyên lời nói của ai đó, trong câu có dấu ngoặc kép. Ex: My brother said: “Iam very happy”. Câu gián tiếp(reported speech): là câu tường thuật lại ý của người nói, trong câu không có dấu ngoặc kép. Ex: My brother said that he was very happy. *Lưu ý: Khi chuyển câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp ta phải thay đổi: chủ ngữ, tân ngữ, thì động từ, các trạng từ, tính từ chỉ sự sở hữu, các từ chỉ thời gian, nơi chốn và các từ chỉ sự xa gần. Những thay đổi khi chuyển câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp. I.Đổi thì động từ Thì của các động từ trong lời nói gián tiếp thay đổi theo một nguyên tắc chung là lùi về quá khứ (các thì xuống cấp) - Thông thường: Direct speech Indirect speech Examples Simple present Simple past He said, “I feel sick.” → He said he felt sick. “I don’t know what Ann is doing”. ->She didn’t know what Ann was doing. Present continuous Past continuous She said, “I’m writing a letter.” → She said she was writing letter. Simple past Present perfect Past perfect He said, “I have seen that film.” → He said he had seen that film. Past continuous Present perfect continuous Past perfect continuous He said, “I was living in New York.” → He said he had been living in New York. He said, “I have been playing football.” ->He said that he had been playing football. Past perfect Past perfect He said, “I had written the letter by 8 o’clock.” -> He said that he had written the letter by 8 o’clock. Past perfect continuous Past perfect continuous He said, “I had been waiting for an hour.” -> He said that he had been waiting for an hour. Will/Shall/May/Can Would/Should/Might/ Could (be able to) He said, “I shall go to Japan in July.” (Simple future) → He said he should go to Japan in July. (Future in the past) He said, “I’ll be writing at 3 o’clock in the afternoon.” ->He said that he would be writing at 3 o’clock in the afternoon. Must/Have to Had to/ would have to II- Thay đổi ngôi trong câu trực tiếp & gián tiếp. Các đại từ nhân xưng và đại sở hữu khi chuyển từ lời nói trực tiếp sang lời nói gián tiếp thay đổi như bảng sau: ĐẠI TỪ CHỨC NĂNG TRỰC TIẾP GIÁN TIẾP Đại từ nhân xưng Chủ ngữ I he, she we They you They Tân ngữ me him, her us Them you Them Đại từ sở hữu Phẩm định my his, her our Their your Their Định danh mine his, her ours Theirs yours Theirs Những trường hợp không tuân theo quy tắc trên. Khi động từ thông báo (say/tell/....) ở các thì hiện tại đơn, hiện tại tiếp diễn, hiện tại hoàn thành hoặc tương lai đơn thì không cần lùi thì động từ. Ex: He says/is saying/has said/will say “The test is easy”. He says/is saying/has said/will say (that) the test is easy. Khi câu trực tiếp diễn tả một sự thật hiển nhiên, một chân lí hay một hành động đk lặp đi lặp lại thường xuyên thì các động từ trong câu gián tiếp vẫn không thay đổi. Ex:- Yesterday the teacher said, “The earth goes round the sun.” Yesterday the teacher said (that) the earth goes round the sun. He said, “My father always drinks coffee after dinner.” He said (that) his father always drinks coffee after dinner. Khi mệnh đề trực tiếp là một thức giả định. Ex: She said: “ If I were you, I wouldn’t tell lies”. She said (that) if she was me, she wouldn’t tell lies. * Đối với các động từ khuyết thiếu: would, could, might, ought, should thường không thay đổi trong câu trần thuật. Ex: He said: “You could go home.” He said (that) I could go home. Tuy nhiên nếu câu nói có một điều kiện không thể xảy ra trong hiện tại thì khi tường thuật ta phải biến đổi thành dạng: could/would have P2 Ex: She said: “If I have enough money, I could buy that dictionary.” She said that if she had enough money she could have bought that dictionary. Khi động từ trong mệnh đề trực tiếp ở thì quá khứ đơn theo đó là một năm cụ thể. Ex: He said “He was born in 2002” He said that he was born in 2002. III- Những thay đổi liên quan đến khái niệm gần xa trong không gian và thời gian. Direct speech Indirected speech This That These Those Today That day Tonight That night Now Then At the moment At that moment Tommorow The next/following day Last week The week before/The previous week Here There Ago Before Yesterday The day before Next week The next/following week Right now Right then The day after tomorrow. In two day’s time/two days after The day before yesterday. Two days before. Ví dụ: Trực tiếp: "I saw the school-boy here in this room today." Gián tiếp: She said that she had seen the school-boy there in that room that day. Trực tiếp: "I will read these letters now." Gián tiếp: She said that she would read those letters then. Ngoài quy tắc chung trên dây, người học cần nhớ rằng tình huống thật và thời gian khi hành động được thuật lại đóng vai trò rất quan trọng trong khi chuyển từ lời nói trực tiếp sang lời nói gián tiếp. Lưu ý: Các suy luận logic về mặt thời gian, nơi chốn là cần thiết khi nói câu nói gián tiếp - Nếu lời nói và hành động xảy ra cùng ngày thì không phải đổi trạng từ chỉ thời gian. At breakfast morning, he said: “I will be busy today”. → At breakfast morning, he said he would be busy today. - Đặc biệt, nếu lúc tường thuật mà điểm thời gian được đưa ra trong lời nói gián tiếp vẫn chưa qua, thì của động từ và trạng từ chỉ thời gian thay đổi hợp lý hoặc không đổi: (On Monday) he said: “I’ll be leaving on Wednesday”. (On Tuesday) he said he will be leaving tomorrow. He said, “I will come to your house tomorrow.” => He said that he will come to my house tomorrow. - Nếu tường thuật cùng địa điểm, cùng thời gian thì chúng ta không thay đổi động từ, từ chỉ định, trạng từ nơi chốn và thời gian: He said, “I will come here to take this book tonight.” => An hour ago he said that he will come here to take this book tonight. - Thêm liên từ vào lời nói gián tiếp: She said, “I am very tired. I’ve been writing for four hours.” She said that she was very tired because/as she had been writing for 4 hours. Một số công thức chuyển câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp. Commands and requests (Câu đề nghị và yêu cầu). +) S + asked/told/wanted + O +(not) + to-V Ex1: He said “Come in,please.” He asked me to come in. Ex2: “Could you help me with this bag?” said the old lady. The old lady told me to help her with that bag. Advice (Lời khuyên) +) S1 + said(that) + S2 + should/should’t + V ought to need/needn’t (didn’t) need to (didn’t) have to +) S + adviced + O + (not) + to-V Ex1: My mother said: “You shouldn’t stay up too late at night.” My mother said (that) I shouldn’t stay up too late at night. My mother adviced me not to stay up too late at night. Questions. Yes/no questions. S1 + asked (O) + if/whether +S2 + V (lùi 1 thì) wanted to know wondered Ex1: Hoa said: “Are you from Hanoi, Mai?” Hoa asked Mai if she was from Hanoi. Ex2: He said to me: “Do you go to school everyday?” He asked to me whether I went to school everyday. Wh-questions. +) S1 + asked (O) + WH word +S2 + V(lùi 1 thì) wanted to know wondered Ex 1: He said: “Where are you going, Hoa?” Hoa asked Hoa where she was going. Ex 2: My mother said: “What will teh weather be tomorrow?” My mother wondered what the weather would be the next day. Declarative sentences (Câu trần thuật) +) S1 + said + (that) + S2 + V (lùi 1 thì) told (O) Ex 1: Tuan said: “ Iam doing my homework now.” Tuan said that he was doing his homework then. Chú ý: Chỉ đổi thì động từ chứ không đổi dạng động từ. Ex: The mother said her son: “Don’t stand there doing nothing.” The mother told her son not to stand there doing nothing
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 ly_thuyet_cau_truc_tiep_cau_gian_tiep.docx
ly_thuyet_cau_truc_tiep_cau_gian_tiep.docx