Đề thi khảo sát chất lượng THPT Quốc gia lần 3 môn Tiếng Anh - Năm học 2016-2017 - Trường THPT Chuyên Vĩnh Phúc (Có đáp án)
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Đề thi khảo sát chất lượng THPT Quốc gia lần 3 môn Tiếng Anh - Năm học 2016-2017 - Trường THPT Chuyên Vĩnh Phúc (Có đáp án)", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
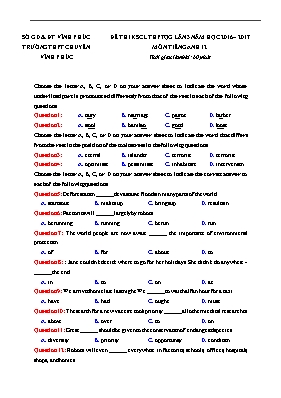
SỞ GD & ĐT VĨNH PHÚC TRƯỜNG THPT CHUYÊN VĨNH PHÚC ĐỀ THI KSCL THPTQG LẦN 3 NĂM HỌC 2016 – 2017 MƠN TIẾNG ANH 12 Thời gian làm bài: 60 phút Choose the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word whose underlined part is pronounced differently from that of the rest in each of the following questions Question 1: A. carry B. marriage C. parrot D. barber Question 2: A. stool B. bamboo C. good D. loose Choose the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word that differs from the rest in the position of the main stress in the following questions Question 3: A. eternal B. islander C. terrorist D. terrorist Question 4: A. optimistic B. pessimistic C. inhabitant D. intervention Choose the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct answer to each of the following questions Question 5: Deforestation ______ devastative floods in many parts of the world. A. starts out B. makes up C. brings up D. results in Question 6: Factories will ______ largely by robots. A. be running B. running C. be run D. run Question 7: The world people are now aware ______ the importance of environmental protection. A. of B. for C. about D. to Question 8: : Jane couldn’t decide where to go for her holidays. She didn’t do anywhere ______ the end. A. in B. to C. on D. at Question 9: We arrived home late last night. We ______ to wait half an hour for a taxi. A. have B. had C. ought D. must Question 10: The search for a new vaccine took priority ______ all other medical researches. A. above B. over C. to D. on Question 11: Great ______ should be given to the conservation of endangered species. A. diversity B. priority C. opportunity D. condition Question 12: Robots will even ______ everywhere in factories, schools, offices, hospitals, shops, and homes. A. seen B. see C. saw D. be seen Question 21: At last, we succeeded in persuading those boys and girls to join our picnic. A. At the end B. In the end C. Lastly D. Endlessly Choose the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the word that is OPPOSITE in meaning to the underlined part in each of the following questions Question 22: “That is a well-behaved boy whose behavior has nothing to complain about.” A. behaving cleverly B. behaving nice C. good behavior D. behaving improperly Question 23: He mentioned in particular electronics, his major at university. A. one and all B. in general C. on whole D. in all Choose the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the most suitable response to the following exchanges. Question 24: “You haven’t been to the bank today, have you?” “______.” A. No, I haven’t. I’m about to. B. Yes, I haven’t. I’m busy. C. No, I haven’t any money. D. No, I have. I got some money. Question 25: Peter: “What a great haircut, Lucy!” Lucy: “_____.” A. Thanks. It’s very kind of you to do this B. You think so? I think it’s a bit too short C. Oh yes, It’s very unfashionable D. It’s my pleasure. Read the following passage and choose the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct word or phrase that best fits each of the numbered blanks Why is it that many teenagers have the energy to play computer games until late at night but can’t find the energy to get out of bed (26) __________ for school? According to a new report, today’s generation of children are in danger of getting so (27)________ sleep that they are putting their mental and physical health at (28)_________. Adults can easily survive on seven to eight hours’ sleep a night, (29)____________teenagers require nine or ten hours. According to medical experts, one in five youngsters (30)___________ anything between two and five hours’ sleep a night less than their parents did at their age. Question 26: A. behind time B. at time C. about time D. in time Question 27: A. few B. less C. little D. much Question 28: A. threat B. jeopardy C. danger D. risk Question 29: A. whereas B. so C. or D. because Question 30: A. brings B. puts C. makes D. gets Read the following passage and choose the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions BLUE MOON “Blue Moon” is a term that is used to describe the phenomenon of a second full moon occurring in one month. How could two full moons possibly occur in a single month? It is not nature’s fault; the natural phrases of the moon do not perfectly match up with the Roman calendar. Although still used today, this calendar was devised by Julius Caesar and Augustus Caesar over 2000 years ago. While the calendar works well, the method that they used does not match the lunar cycle exactly. Thus, occasionally the moon will go through its “full” phrase twice before the month changes. A “blue moon” is an uncommon event. And it rare occurrence of a eventually led to the usage of the phrase “once in a blue moon”. This phrase was commonly used to indicate an event that could never happen. Over time, the meaning of the phrase changed from something that seldom happens. Today, this phrase is used to indicate extremely rare events, the absurd, or things that never happen. Question 31: What is the main purpose of this passage? A. To illustrate the features of the moon. B. To inform readers of the difference between the Roman calendar and the lunar calendar C. To explain the definition and the usage of “blue moon” D. To support the importance of the lunar calendar Question 32: According to the passage, to what does the term “blue moon” refer to? A. Events that could never happen B. The second full moon in one month C. A moon with the color blue D. Cold nights causing the moon to appear blue Question 33: The word “phrase” in the passage is closet in meaning to A. Position B. Cycle C. Shape D. Influence Question 34: Why doesn’t our calendar match the lunar cycle exactly? A. Our calendar was designed by humans B. It has more days than it sound C. The lunar cycle is wrong D. Our calendar was not designed by humans Question 35: The word “absurd” in the passage is closet in meaning to A. Ridiculous B. Frequent C. Normal D. Interesting Question 36: According to the passage, which of the following is NOT true? A. The meaning of the “blue moon” changed over the years. B. The Roman calendar was invented by Julius Caesar and Augustus Caesar C. The phrase “once in a blue moon” could refer to two people eating dinner together D. The Roman calendar is still in use today. Question 37: Which of the following can be inferred from the passage? A. The phrase “blue moon” refers to the frequency of events B. The Roman calendar matches the natural phrases of the moon. C. The usage of “blue moon” has not changed. D. Two full moons often occur in one month. Read the following passage and choose the letter A, B, C, or D on your answer sheet to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions Many flowering plants woo insect pollinators and gently direct them to their most fertile blossoms by changing the color of individual flowers from day to day. Through color cues, the plant signals to the insect that it would be better off visiting one flower on its bush than another. The particular hue tells the pollinator that the flower is full of far more pollen than are neighboring blooms. That nectar-rich flower also happens to be fertile and ready to disperse its pollen or to receive pollen the insect has picked up from another flower. Plants do not have to spend precious resources maintaining reservoirs of nectar in all their flowers. Thus, the color-coded communication system benefits both plants and insects. For example, on the lantana plant, a flower starts out on the first day as yellow, when it is rich with pollen and nectar. Influenced by an as-yet-unidentified environmental signal, the flower changes color by triggering the production of the pigment anthromyacin. It turns orange on the second day and red on the third. By the third day, it has no pollen to offer insects and is no longer fertile. On any given lantana bush, only 10 to 15 per cent of the blossoms are likely to be yellow and fertile. But in tests measuring the responsiveness of butterflies, it was discovered that the insects visited the yellow flowers at least 100 times more than would be expected from haphazard visitation. Experiments with paper flowers and painted flowers demonstrated that the butterflies were responding to color cues rather than, say, the scent of the nectar. In other types of plants, blossoms change from white to red, others from yellow to red, and so on. These color changes have been observed in some 74 families of plants. Question 38: The first paragraph of the passage implies that insects benefit from the color-coded communication system because_______ A. they can gather pollen efficiently. B. the colors hide them from predators. C. the bright colors attract fertile females D. other insect species can not understand the code. Question 39: The word “woo” is closest in meaning to_______ A. frighten B. trap C. deceive D. attract Question 40: The word “it” refers to_______ A. a plant B. a blossom C. an insect D. a signal Question 41: The word “hue” is closet in meaning to_______ A. smell B. shape C. texture D. color Question 48: My grandfather started collecting stamps when he was 65. A. My grandfather took up stamps collecting when he was 65. B. My grandfather took off stamps collecting when he was 65. C. My grandfather took away stamps collecting when he was 65. D. My grandfather took in stamps collecting when he was 65. Question 49: We didn’t get home until it was almost dark. A. It was almost dark, which prevented us from getting home. B. We decided to go home when it grew dark. C. Since it was almost dark, we decided not to go home. D. It was almost dark when we got home. Question 50: Peter woke up early because he didn’t want to miss his flight. A. Peter woke up early so that he wouldn’t miss his flight. B. If Peter had woken up early, he wouldn’t have missed his flight. C. Waking up early, Peter didn’t miss his flight. D. As Peter woke up early, he was unlikely to miss his flight. Đáp án 1-D 2-B 3-A 4-C 5-D 6-C 7-A 8-A 9-B 10-B 11-A 12-D 13-C 14-C 15-A 16-C 17-NA 18-B 19-D 20-B 21-B 22-D 23-D 24-A 25-B 26-D 27-C 28-D 29-A 30-D 31-C 32-B 33-B 34-A 35-A 36-C 37-A 38-A 39-D 40-C 41-D 42-B 43-C 44-A 45-D 46-C 47-B 48-A 49-D 50-A LỜI GIẢI CHI TIẾT Question 1: Đáp án D carry /'kỉri/ marriage /'mỉridʒ/ parrot /'pỉrət/ barber /'bɑ:bə/ Question 2: Đáp án B stool /stu:l/ bamboo /bỉm'bu:/ good /gud/ loose /lu:s/ Question 3: Đáp án A Phần A trọng âm rơi vào âm tiết thứ 2, cịn lại là thứ nhất eternal /i'tɜ:nl/ islander /'ailəndə[r]/ terrorist /'terərist/ subsidy /'sʌbsidi/ Question 4: Đáp án C Phần C trọng âm rơi vào âm tiết thứ 2, cịn lại là thứ 3 optimistic /,ɒpti'mistik/ pessimistic /,pesi'mistik/ inhabitant /in'hỉbitənt/ intervention /,intə'ven∫n/ Question 5: Đáp án D Result in: để lại kết quả ở cái gì start out: khởi hành make up: trang điểm, quyết định, dọn gọn ghẽ, bring up: đem lên, mang lên; nuơi nấng, giáo dục, dạy dỗ Dịch: Nạn phá rừng tạo hậu quả nhiều cơn lũ tàn phá ở nhiều nơi trên thế giới Question 6: Đáp án C Ở đây chủ ngữ là Factories (vật) => câu được chia ở dạng bị động Will be run: sẽ được điều hành Dịch: Các nhà máy sẽ được vận hành phần lớn bởi robo Question 7: Đáp án A Cấu trúc: To be aware of something: nhận biết, biết về cái gì Dịch: Người dân trên thế giới hiện nay nhận thức được tầm quan trọng của bảo vệ mơi trường. Question 8: Đáp án A Phân biệt giữa in the end và at the end: - at the end: cuối, phía cuối, phần cuối (của cái gì, ví dụ: cuối tháng at the end of the month, cuối sự kiện at the end of the event,) - in the end = finally, eventually = cuối cùng => chọn in the end Dịch: Jane khơng thể quyết định nên đi nghỉ ở đâu. Cuối cùng cơ ấy khơng đi đâu cả. Question 9: Đáp án B Must + V (khơng cĩ giới từ to) => D loại Ought to: nên => về nghĩa trong câu thì khơng phù hợp => loại Trong câu đang dùng thì quá khứ, do đĩ khơng thể sử dụng have => loại Đáp án: had to: phải Dịch: Tối qua chúng tơi về nhà muộn. Chúng tơi đã phải đợi taxi nửa tiếng Question 10: Đáp án B Cấu trúc take priority over something: ưu tiên, đặt hàng đầu Dịch: Việc tìm một vacxin mới chiếm ưu tiên trên mọi nghiên cứu khác Question 45: Đáp án D Từ " haphazard" là gần nhất trong ý nghĩa với từ nào sau đây? A. may mắn B. kỳ vọng C. Nguy hiểm D. ngẫu nhiên Haphazard ~ random: lộn xộn, ngẫu nhiên it was discovered that the insects visited the yellow flowers at least 100 times more than would be expected from haphazard visitation. nĩ đã được phát hiện ra rằng các lồi cơn trùng đã ghé thăm những bơng hoa màu vàng hơn ít nhất 100 lần so với dự đốn các cuộc ghé thăm ngẫu nhiên Question 46: Đáp án C All the guests enjoyed themselves at the party apart from George. Tất cả khách đều cảm thấy vui thích ở bữa tiệc ngoại trừ George. = C. George was the only one guest who didn’t enjoy himself at the party. George là khách duy nhất khơng vui thích ở bữa tiệc A. George khơng thích bữa tiệc như các khách khác B. George là khách duy nhất nghĩ bữa tiệc đáng vui thích D. George, khơng như các khách khác, cĩ khoảng thời gian vui vẻ tại bữa tiệc Question 47: Đáp án B It was Jane who came up with the idea for the sales promotion. Đĩ là Jane người đã đưa ra ý tưởng cho việc thúc đẩy bán hàng. = B. Jane was the brain behind the sales promotion. Jane là bộ não đằng sau việc thúc đẩy bán hàng A. Jane hồn tồn bị ám ảnh với việc thúc đẩy bán hàng C. Bán hàng tăng là thành quả của sự cố gắng của Jane D. Khơng ai ngồi Jane thích ý tưởng cho việc thúc đẩy bán hàng Question 48: Đáp án A My grandfather started collecting stamps when he was 65. Ơng tơi bắt đầu sưu tập tem khi ơng 65 tuổi = A. My grandfather took up stamps collecting when he was 65. Take up = start doing st: bắt đầu làm một việc gì Question 49: Đáp án D We didn’t get home until it was almost dark. Chúng tơi khơng về đến nhà cho đến tận khi trời gần tối = D. It was almost dark when we got home. Trời đã gần tối khi chúng tơi về đến nhà A. Trời gần tối, điều này ngăn cản chúng tơi về nhà B. Chúng tơi quyết định về nhà khi trời tối C. Bởi vì trời gần tối, chúng tơi quyết định ko về nhà Question 50: Đáp án A Peter woke up early because he didn’t want to miss his flight. Peter dậy sớm vì anh ko muốn lỡ chuyến bay = A. Peter woke up early so that he wouldn’t miss his flight. Peter dậy sớm để anh ấy sẽ ko bị lỡ chuyến bay B. Nếu Peter dậy sớm, anh ấy đã ko bị lỡ chuyến bay C. Dậy sớm, Peter ko bị lỡ chuyến bay D. Bởi Peter dậy sớm, anh ấy khả năng ko lỡ chuyến bay Eroguseriotv ueriobyjserotvjerm90buyjmuu6490uitv523490k34icr-04itv90utcrik3490tvukci3vikc-0ewiltv-0itvktcrl234ict34tvbkyeyhserhasegh Eroguseriotv ueriobyjserotvjerm90buyjmuu6490uitv523490k34icr-04itv90utcrik3490tvukci3vikc-0ewiltv-0itvktcrl234ict34tvbkyeyhserhasegh
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 de_thi_khao_sat_chat_luong_thpt_quoc_gia_lan_3_mon_tieng_anh.doc
de_thi_khao_sat_chat_luong_thpt_quoc_gia_lan_3_mon_tieng_anh.doc