Bài tập bổ trợ môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 12 - Unit 2: Cultural diversity
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Bài tập bổ trợ môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 12 - Unit 2: Cultural diversity", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
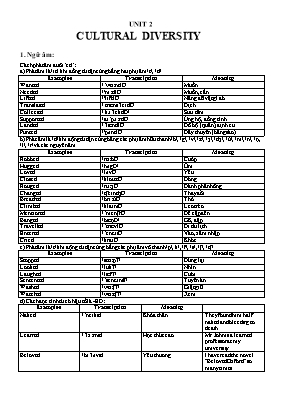
UNIT 2 CULTURAL DIVERSITY 1. Ngữ õm: Cỏch phỏt õm đuụi ‘ed’: a) Phỏt õm là /ɪd/ khi đồng từ tận cựng bằng hai phụ õm /t/, /d/ Examples Transciption Meaning Wanted /ˈwɑːntID/ Muốn Needed /'niːdID/ Muốn, cần Lifted /'lɪftID/ Nõng đỡ vật gỡ đú Translated / trổnsˈleɪtID/ Dịch Collected / kəˈlektID / Sưu tầm Supported /səˈpɔːrtID/ Ủng hộ, đồng tỡnh Landed /ˈlổndID/ Đổ bộ (quõn); định cư Punted /'pʌntID/ Đẩy thuyền (bằng sào) b) Phỏt õm là /d/ khi động từ tận cựng bằng cỏc phụ õm hữu thanh /b/, /g/, /v/, /z/, /ʒ/, /dʒ/, /ð/, /m/, /n/, /ŋ, /l/, /r/ và cỏc nguyờn õm Examples Transciption Meaning Robbed /rɑːbD/ Cướp Hugged /hʌgD/ ễm Loved /lʌvD/ Yờu Closed /kloʊzD/ Đúng Rouged /ruːʒD/ Đỏnh phấn hồng Changed /tʃeɪndʒD/ Thay đổi Breathed /briːðD/ Thở Climbed /klaɪmD/ Leo trốo Mentioned /ˈmenʃnD/ Đề cập đến Banged /bổŋD/ Gừ, đập Travelled /ˈtrổvlD/ Đi du lịch Entered /ˈentərD/ Vào, xõm nhập Cried /kraɪD/ Khúc c) Phỏt õm là /t/ khi động từ tận cựng bằng cỏc phụ õm vụ thanh /p/, k/, /f/, /s/, /ʃ/, /tʃ/ Examples Transciption Meaning Stopped /stɑːpT/ Dừng lại Looked /lʊkT/ Nhỡn Laughed /lổfT/ Cười Sentenced /ˈsentənsT/ Tuyờn ỏn Washed /wɑːʃT/ Giặt giũ Watched /wɑːtʃT/ Xem d) Cỏch đọc tớnh từ cú hậu tố là -ED: Examples Transciption Meaning Naked /ˈneɪkɪd/ Khỏa thõn They found him half naked and bleeding to death Learned /ˈlɜːrnɪd/ Học thức cao Mr.John is a learned professor at my university Beloved /bɪˈlʌvɪd/ Yờu thương I have read the novel "Beloved Oxford" so many times Aged /ˈeɪdʒɪd/ Rất già My grandmother is aged Blessed /ˈblesɪd/ May mắn He is really a blessed man Dogged /ˈdɔːɡɪd/ kiờn trỡ, bền bỉ It's dogged that does it Crooked /ˈkrʊkɪd/ quanh co, khỳc khuỷu This road is very crooked Ragged /ˈrổɡɪd/ xơ xỏc, tả tơi There is a man sitting over there in a ragged jacket Rugged /ˈrʌɡɪd/ xự xỡ, gồ ghề The countryside around here is very rugged Cursed /ˈkɜːrsɪd/ tức giận, khú chịu She seemed to be cursed because of waiting for me too long Sacred /ˈseɪkrɪd/ thiờn liờng, trõn trọng Human life must always be sacred Wicked /ˈwɪkɪd/ xấu xa, độc ỏc That was very wicked of you Wretched /ˈretʃɪd/ khốn khổ, bất hạnh She doesn't want to lead a wretched existence in the slums One/two/four-legged /...-ˈleɡɪd/ 1/2/4 chõn Cats are four-legged animals 2. Ngữ phỏp và cấu trỳc: Review of tenses : Verb Tense Revision Chart (Revision of all tenses of English verbs with a brief explanation and an example.) FORM TENSE USE EXAMPLE S + V_O/E/ES / am/is/are Present Simple *Regular activities / routine. 1. We play tennis on Sunday. S + am/is/are + V_ing Present Continuous *Continuous present action. 1. The children are playing at the moment. S + have/has + V_3/ed Present Perfect Simple *Finished part of continuous action. *Completed actions in unfinished time period. *Recent events (unspecified time) *Past action with a result in the present. *Experiences up to now. 1. They have played two sets. 2. They have played several other matches this year. 3. Their parents have just arrived. 4. Sue has broken her bike so she can’t continue. 5. They have played in many tournaments. S + have/has + been + V_ing Present Perfect Continuous *Actions begun in the past which continue today. 1. They have been playing badminton since 3 o’clock this afternoon. S + V_2/ed / was / were Past Simple *Finished actions at a specific time in the past. 1. Last Saturday we went fishing. S + was/were + V_ing Past Continuous *Past continuous actions. 1. At 3.30 pm they were watching their favorite film. S + had + V_3/ed Past Perfect Simple *Completed actions before a specific time or event in the past. 1. Two other people had played a match before we arrived. S + had + been + V_ing Past Perfect Continuous *Continuous actions before a specific time or event in the past. 1. At 4pm we had been playing for 2 hours. S + will + V_O Future Simple *Predictions *Spontaneous decisions/offers 1. They will win the match today. 2. I’ll lend you my money! S + will + be + V_ing Future Continuous *Continuous future action 1. Tomorrow they will be playing in another club. S + will + have + V_3/ed Future Perfect *Completed future action 1. By September they will have finished three courses. S + will have been + V_ing Future Perfect Continuous *Continuous future action estimated at a time in the future. 1. At 5pm we will have been playing for 3 hours. BÀI TẬP I. Choose the best answer for each of the following sentences. 1. Since I ______ young, I have always known that the conical leaf hat or the “nún lỏ” is a symbol of Vietnamese culture. A. am B. was C. have been D. had been 2. If you’d written earlier, I’d have known when you ______ to go on holiday. A. would want B. would intend C. wanted D. will want 3. As soon as he _____, tell him to call me back, please. A. will arrive B. arrives C. would arrive D. is arriving 4. This house is often empty because the owners _____ abroad 5 times a year. A. are going B. were going C. used to go D. go 5. Which sentence is correct? A. I’ve been to Japan in 2010. B. He’s been to Japan once. C. I’ve been in Japan once. D. He was in Japn since 2010. 6. You _____ a beautiful cake. It tastes delicious. A. had done B. had made C. have made D. did 7. My aunt _____ in the park when I met her. A. walked B. was walking C. had walked D. had a walking 8. “_____ that letter yet?” – “No, I’m just typing it.” A. Have you written B. Are you writing C. Did you write D. Were you writing 9. As she went out, she ______ sight of herself in the mirror. A. talked B. took C. saw D. caught 10. “When did you last saw or heard from Alan?” – “I _____ him since last month.” A. didn’t met B. haven’t met C. don’t meet D. wasn’t meeting 11. “How long _____ her?” – “Oh, only for a couple of months.” A. have you known B. do you know C. are you knowing D. have you been knowing 12. I very much hope it’ll rain soon. We _____ a drop for over a month. A. didn’t have B. haven’t had C. hadn’t had D. haven’t 13. “Ouch! I _____ my finger!” suddenly said Tom. A. had cut B. have cut C. was cutting D. cut 14. You _____ a university degree for this job. You’ll only have to write letters and answer the phone. A. haven’t got B. mustn’t have C. needn’t D. don’t need 15. The captain of the ocean liner has just asked a sailor if _____ seen a white whale near the African coast. A. had he ever B. he had ever C. he always had D. he has ever 16. “Excuse me, is anybody sitting here?” – “______” A. No, thanks. B. Yes, I am so glad. C. Sorry, the seat is taken. D. You are welcome. 17. The fox tries ______ to reach the fruit high up the tree. A. in fail B. in vain C. in loss D. in hope 18. We have bought extra food ______ our friends stay to dinner. A. if only B. whether C. in case D. only when 19. If you want to get better, do exactly ______ your doctor tells you. A. like B. the same C. as D. alike 20. Lomonosov was not _____ a great scientist but also a very talented poet. A. fairly B. merely C. hardly D. scarcely 21. When the results of the fraud investigation were announced last week, the staff came up smelling of ______. A. roses B. money C. perfume D. gold 22. The attitude of experts ______ the execution of endomyocardial biopsy at ARVD is contradictory. A. towards B. above C. beneath D. with 23. Lisa walked into the room and struck a/an ______ , hoping she would be noticed. A. chord B. act C. deal D. pose 24. It is important to have someone you can _______ in. A. trust B. hide C. confide D. declare 25. Millions of people say Coke tastes best from a bottle, and whether this is scientifically provable or not, these millions know what they like: the look of the bottle and the way it fits so ______ into the hand. A. neatly B. orderly C. tidily D. finitely 26. Once I could see light at the end of the ______, writing the last part of the book wasn’t so hard. A. tunnel B. subway C. passage D. journey 27. The growing use of air conditioning and refrigeration risks ______ international efforts to cut emissions to avoid dangerous heatwaves, extreme weather and sea level rise. A. undermine B. undermining C. to undermine D. undermined 28. In its rich ______, culture has intrinsic value for development as well as social cohesion and peace. A. diverse B. diversity C. diversify D. diversification 29. In Viet Nam, the Ao Dai is the ______ dress for women, and it is now standard for weddings, for celebrating Tet and for other formal occasions. A. splendid B. pulchritude C. deliverable D. traditional 30. One of the biggest temptations for someone new to the travel game is to look at everything from behind rose-tinted ______, and this typically comes out in their writing. A. mirrors B. glasses C. patterns D. prospects 31. She really went out on a ______ when she criticised the professor in front of the whole class. A. limb B. leg C. lung D. lip 32. Studies show that children who are exposed to a more diverse community are more creative and ______ of differences. These students learn how to resolve conflict more easily. A. tolerate B. tolerant C. tolerance D. tolerated 33. In love marriages, people prefer to choose their partners on their own, while in case of ______ marriage or arranged marriages others prefer partners chosen by their family or parents. A. contractual B. romantic C. obliged D. sacrificed 34. Vietnamese spend a lot of time in preparing ______. The Western people, especially, don’t spend too much time for cooking. A. grocery B. beverage C. drink D. food 35. For a long time, the images of young ladies with a conical leaf hat known as “Non la” has made a strong impression on _______ coming to Viet Nam A. who B. whom C. whoever D. whose 36. They got married without their parents’ _____. A. blessing B. vow C. swear D. prayer 37. The show starts with a welcome of the _______ who introduces guests or entertainers at a formal occasion. A. bridesmaid B. bridegroom C. master chief D. master of ceremony 38. We haven’t ______ all the details yet, but we’ll certainly be going to the USA in July. A. concluded B. terminated C. ceased D. finalised 39. In her speech the Prime Minister ______ tribute to the valuable contributions to society made by voluntary organisations. A. gave B. paid C. sent D. brought 40. The weather is going to change soon – I can feel it in my ______. A. skin B. teeth C. legs D. bones 41. There is a very strong movement now against ______ sports like hunting or shooting. A. blood B. death C. killing D. terminal 42. Maria and Jean had a ______ romance – they met and married within two months. A. cyclone B. hurricane C. whirlwind D. typhoon 43. If you say you’d like ______ of cream on your strawberries then you don’t want very much cream. A. a dollop B. a dash C. oodles D. lashings 44. I’m afraid we got our ______ crossed – I thought my husband would be picking up the children and he thought I was doing it. A. fingers B. minds C. purposes D. wires 45. After the football match the crowds _____ out of the stadium into the nearest bars and cafes. A. leaked B. poured C. trickled D. dripped 46. Alexandre Gustave Eiffel was born to a family known for fine craftwork of wood and ______ of coal. A. manicurists B. merchants C. mechanics D. miners 47. His breaking the rules set a dangerous ______. A. custom B. precedent C. practice D. tradition 48. In recent years there has been a ______ increase in the cost of living. A. powerful B. ponderous C. wide D. significant 49. When a Vietnamese wants to work part-time in Australia, he needs to get a work ______. A. permit B. permission C. permissibility D. permissiveness 50. The river was ______ to help the local children go to school easily. A. bridged B. demolished C. tied D. hanged II. Read the passage below and choose one correct answer for each question: INDIAN MARRIAGES Marriage is one of the oldest human institutions and this is as true in Indian culture as anywhere else. In India marriage, called “Kanyadana" or “donating a virgin”, is thought of as the greatest sacrifice that a father can make and for the groom as an obligation to perpetuate his bloodline. Many people believe that a marriage is still binding after death. In early times girls were thought to be ready for marriage after puberty and later even children could be married. Divorce and remarriage were not always possible. By Medieval times Marriage was compulsory for girls, who very often married between the ages of eight and nine. Among those able to afford it, polygamy was common and rulers would often have one wife from their own region and other minor wives from other areas. Now, divorce and remarriage is possible and non-Muslim Indian men can only have one wife. Although are many regional variations, some features of the Indian wedding ceremony are similar throughout the country. In general weddings are very complicated events and involve long negotiations about dowry payments prior to the event. After this has been decided a day is chosen by asking an astrologer to find a lucky day. Preparations begin early because a marriage is not only one of the highlights a person’s life, but a large and complex social gathering to organize. The night before, the bride, her friends and female relatives gather together for a party called a “mehendi”, where they paint each other’s hands and feet with Henna and dance and listen to music. Her guests often give the bride advice about married life and tease her about her future husband. Weddings are traditionally held at the bride’s home or in a temple, but parks, hotels and marriage halls are becoming increasingly popular. On the day a wedding altar or “mandapa” is built and covered in flowers. All of the wedding ceremony will be held in the altar. The clothing a couple wear on their wedding day varies between regions and ethnic groups. Women most commonly wear a sari. The bride wears a lot of jewelry as this symbolizes the prosperity she will bring to her new family. In the South wearing flowers is common. The groom wears traditional costume or a suit. Turbans are also popular headgear. The ceremony begins with a mixture of tumeric, sandlewood paste and oils being applied to the couples face and arms. In the past this was done to the whole body, but now it is only symbolic, with only a little being rubbed on. Then they are showered in flowers. After this they perform the rituals that will make them man and wife. First they garland each other and then take seven symbolic steps together representing seven gifts and seven promises. Finally they say the vows and then they are legally married. The bride’s father or guardian takes her hands and puts them in her husband’s giving her to him. Now she is no longer a member of her father’s family, but a member of her husband’s. They then touch the feet of their elders for luck. After the wedding ceremony, the couple go to the groom’s house. The bride should be careful to enter the house right foot first for luck. In the evening and late into the night the families and their guests celebrate with dancing, music and food. 1. In India weddings are _______. A. a duty for the man to continue his family B. thought to end at death C. a duty for the father D. seen asa benefit for the father 2. Divorce and remarriage ______. A. are only possible for non-Muslims B. were sometimes not possible in the past C. have always been possible D. have only become possible in modern times 3. Indian weddings ______. A. are straightforward and brief B. are thought to be lucky C. are intricate and time consuming D. involve only the immediate family 4. The evening prior to the wedding, the wife-to-be is given recommendations about ______. A. married life B. her future husband C. a “mehendi” party D. wedding gifts 5. The wedding ceremony is conducted in a special _______. A. temple B. hotels and marriage halls C. park or pagoda D. wedding altar or “mandapa” 6. The gold and jewels the bride wears represent _______. A. tradition B. popularity C. prosperity C. poverty 7. These days the materials applied prior to the ceremony are only ______. A. invaluable B. specific C. particular D. symbolic 8. After the wedding, the bride has left _______. A. her father’s family B. her husband’s family C. his father’s family D. his husband’s family 9. It is important that the new bride goes into the new house with _______. A. her first lucky B. her right foot first C. her first talk D. her left foot first 10. The word “complex” in paragraph 3 means ______. A. complicated B. simple C. formal D. significant III. Read the passage below and choose one correct answer for each question: Many people think that we can learn a lot about the culture of a foreign country simply by living in that country. However, this is not necessarily true. Often, the longer we stay in a foreign country, the more we realize how little we actually know about the culture of that country. Books and talks about other people’s culture can even be dangerous because they concentrate on cultural differences and exaggerate national character, and sometimes a lot of information they contain is untrue. In a study recently carried out in Britain, people were asked to make a list of anything that they thought was typical ofBritainand would interest a foreign visitor there. Most mentioned Shakespeare, the Queen, village inns, English folk dancing, English castles, and fish chips wrapped in newspaper. Although all of these characters can be found in British culture, they do not show the real interests of ordinary British people: (they are, in fact, simply stereotype - that is, general character which people wrongly think are typical). What is surprising is that they were suggested by British people themselves as representing their culture. If people have such a wrong impression of their own culture, how much false would their impression of their culture be! 1. If we stay a long time in a foreign country, _______. A. we will usually realize that we know very little about its culture B. we will sometimes forget about culture of our own country C. we can often learn a lot about the culture of the foreign country D. we can seldom find out anything at all about its culture 2. It is hard to learn about a country’s cultural from books because such books _______. A. concentrate on the dangers of the foreign culture B. exaggerate national character C. take no notice of culture different D. contain little information about culture 3. When asked about their own culture, many British people _______. A. gave incorrect answers B. were surprised by the question asked C. argued they know little about British culture D. said they themselves were not typical of British people 4. It can be inferred from the last paragraph that it’s easy to _______. A. give exact information about your own country B. describe stereotypes of your country C. know a lot about your own country’s culture D. know the culture of other countries 5. Which of the following is true? A. It’s easy to assimilate the culture of a foreign country. B. Visitors to a country are soon assimilated into it culture. C. British people understand their own culture more than other culture. D. The culture of a foreign culture can not be learned by reading books. IV. Read the passage below and choose one correct answer for each question: Culture is a strong part of people’s lives. It influences their views, their values, their humor, their hopes, their loyalties, and their w
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 bai_tap_bo_tro_mon_tieng_anh_lop_12_unit_2_cultural_diversit.doc
bai_tap_bo_tro_mon_tieng_anh_lop_12_unit_2_cultural_diversit.doc